目錄
- 一��、前言
- 二、工作流程
- 三�����、數(shù)據(jù)模塊
- 四��、索引模塊
- 五、搜索模塊
一�、前言
這篇文章,我們將會嘗試從零搭建一個簡單的新聞搜索引擎
當然����,一個完整的搜索引擎十分復雜�,這里我們只介紹其中最為核心的幾個模塊
分別是數(shù)據(jù)模塊、排序模塊和搜索模塊��,下面我們會逐一講解���,這里先從宏觀上看一下它們之間的工作流程
二、工作流程
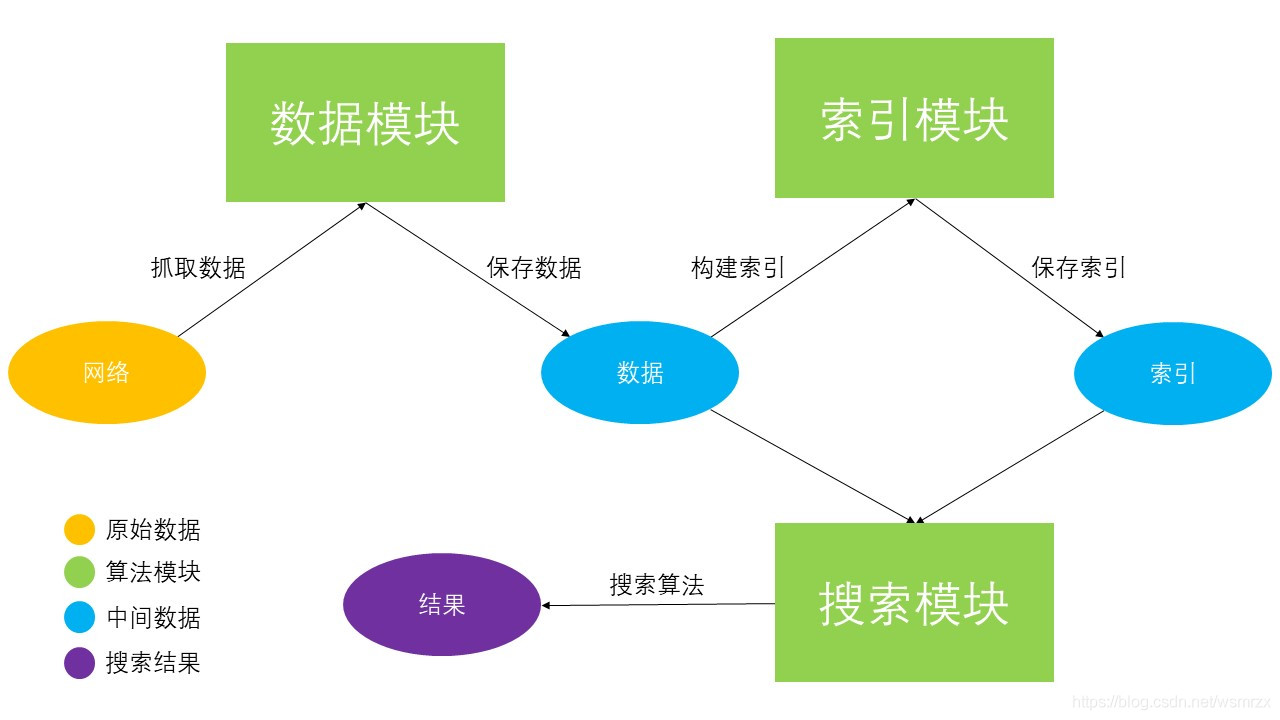
三��、數(shù)據(jù)模塊
數(shù)據(jù)模塊的主要作用是爬取網(wǎng)絡上的數(shù)據(jù)��,然后對數(shù)據(jù)進行清洗并保存到本地存儲
一般來說��,數(shù)據(jù)模塊會采用非定向爬蟲技術廣泛爬取網(wǎng)絡上的數(shù)據(jù)�����,以保證充足的數(shù)據(jù)源
但是由于本文只是演示,所以這里我們僅會采取定向爬蟲爬取中國社會科學網(wǎng)上的部分文章素材
而且因為爬蟲技術我們之前已經(jīng)講過很多�����,這里就不打算細講����,只是簡單說明一下流程
首先我們定義一個數(shù)據(jù)模塊類,名為 DataLoader�����,類中有一個核心變量 data 用于保存爬取下來的數(shù)據(jù)
以及兩個相關的接口 grab_data (爬取數(shù)據(jù)) 和 save_data (保存數(shù)據(jù)到本地)
grab_data() 的核心邏輯如下:
1.首先調(diào)用 get_entry(),獲取入口鏈接
def get_entry(self):
baseurl = 'http://his.cssn.cn/lsx/sjls/'
entries = []
for idx in range(5):
entry = baseurl if idx == 0 else baseurl + 'index_' + str(idx) + '.shtml'
entries.append(entry)
return entries
2.然后調(diào)用 parse4links()���,遍歷入口鏈接���,解析得到文章鏈接
def parse4links(self, entries):
links = []
headers = {
'USER-AGENT': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/67.0.3396.99 Safari/537.36'
}
for entry in entries:
try:
response = requests.get(url = entry, headers = headers)
html = response.text.encode(response.encoding).decode('utf-8')
time.sleep(0.5)
except:
continue
html_parser = etree.HTML(html)
link = html_parser.xpath('//div[@class="ImageListView"]/ol/li/a/@href')
link_filtered = [url for url in link if 'www' not in url]
link_complete = [entry + url.lstrip('./') for url in link_filtered]
links.extend(link_complete)
return links
3.接著調(diào)用 parse4datas(),遍歷文章鏈接���,解析得到文章內(nèi)容
def parse4datas(self, entries):
datas = []
headers = {
'USER-AGENT': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/67.0.3396.99 Safari/537.36'
}
data_count = 0
for entry in entries:
try:
response = requests.get(url = entry, headers = headers)
html = response.text.encode(response.encoding).decode('utf-8')
time.sleep(0.2)
except:
continue
html_parser = etree.HTML(html)
title = html_parser.xpath('//span[@class="TitleFont"]/text()')
content = html_parser.xpath('//div[@class="TRS_Editor"]//p//text()')
content = [cont.replace('\u3000', '').replace('\xa0', '').replace('\n', '').replace('\t', '') for cont in content]
content = [cont for cont in content if len(cont) > 30 and not re.search(r'[《|》]', cont)]
if len(title) != 0 or len(content) != 0:
data_count += 1
datas.append({
'id' : data_count,
'link': entry,
'cont': '\t'.join(content),
'title': title[0]
})
return datas
grab_data() 的核心代碼如下:
def grab_data(self):
# 獲取入口鏈接
entries = self.get_entry()
# 遍歷入口鏈接�,解析得到文章鏈接
links = self.parse4links(entries)
# 遍歷文章鏈接����,解析得到文章內(nèi)容
datas = self.parse4datas(links)
# 將相關數(shù)據(jù)寫入變量 data
self.data = pd.DataFrame(datas)
save_data() 的核心代碼如下:
def save_data(self):
# 將變量 data 寫入 csv 文件
self.data.to_csv(self.data_path, index = None)
至此����,我們已經(jīng)爬取并保存好數(shù)據(jù) data���,數(shù)據(jù)以 DataFrame 形式存儲�,保存在 csv 文件�����,格式如下:
|---------------------------------------------------|
| id | link | cont | title |
|---------------------------------------------------|
| page id | page link | page content | page title |
|---------------------------------------------------|
| ...... | ...... | ...... | ...... |
|---------------------------------------------------|
四�����、索引模塊
索引模型的主要作用是構建倒排索引 (inverted index)���,這是搜索引擎中十分關鍵的一環(huán)
一般來說,構建索引的目的就是為了提高查詢速度
普通的索引一般是通過文章標識索引文章內(nèi)容�����,而倒排索引則正好相反��,通過文章內(nèi)容索引文章標識
具體來說���,倒排索引會以文章中出現(xiàn)過的詞語作為鍵��,以該詞所在的文章標識作為值來構建索引
首先我們定義一個索引模塊類����,名為 IndexModel,類中有一個核心變量 iindex 用于保存倒排索引
以及兩個相關的接口 make_iindex (構建索引) 和 save_iindex (保存索引到本地)
make_iindex() 的核心代碼如下(具體邏輯請參考注釋):
def make_iindex(self):
# 讀取數(shù)據(jù)
df = pd.read_csv(self.data_path)
# 特殊變量�,用于搜索模塊
TOTAL_DOC_NUM = 0 # 總文章數(shù)量
TOTAL_DOC_LEN = 0 # 總文章長度
# 遍歷每一行
for row in df.itertuples():
doc_id = getattr(row, 'id') # 文章標識
cont = getattr(row, 'cont') # 文章內(nèi)容
TOTAL_DOC_NUM += 1
TOTAL_DOC_LEN += len(cont)
# 對文章內(nèi)容分詞
# 并將其變成 {word: frequency, ...} 的形式
cuts = jieba.lcut_for_search(cont)
word2freq = self.format(cuts)
# 遍歷每個詞��,將相關數(shù)據(jù)寫入變量 iindex
for word in word2freq:
meta = {
'id': doc_id,
'dl': len(word2freq),
'tf': word2freq[word]
}
if word in self.iindex:
self.iindex[word]['df'] = self.iindex[word]['df'] + 1
self.iindex[word]['ds'].append(meta)
else:
self.iindex[word] = {}
self.iindex[word]['df'] = 1
self.iindex[word]['ds'] = []
self.iindex[word]['ds'].append(meta)
# 將特殊變量寫入配置文件
self.config.set('DATA', 'TOTAL_DOC_NUM', str(TOTAL_DOC_NUM)) # 文章總數(shù)
self.config.set('DATA', 'AVG_DOC_LEN', str(TOTAL_DOC_LEN / TOTAL_DOC_NUM)) # 文章平均長度
with open(self.option['filepath'], 'w', encoding = self.option['encoding']) as config_file:
self.config.write(config_file)
save_iindex() 的核心代碼如下:
def save_iindex(self):
# 將變量 iindex 寫入 json 文件
fd = open(self.iindex_path, 'w', encoding = 'utf-8')
json.dump(self.iindex, fd, ensure_ascii = False)
fd.close()
至此,我們們經(jīng)構建并保存好索引 iindex��,數(shù)據(jù)以 JSON 形式存儲�,保存在 json 文件,格式如下:
{
word: {
'df': document_frequency,
'ds': [{
'id': document_id,
'dl': document_length,
'tf': term_frequency
}, ...]
},
...
}
五�、搜索模塊
在得到原始數(shù)據(jù)和構建好倒排索引后�����,我們就可以根據(jù)用戶的輸入查找相關的內(nèi)容
具體怎么做呢�?
1.首先我們對用戶的輸入進行分詞
2.然后根據(jù)倒排索引獲取每一個詞相關的文章
3.最后計算每一個詞與相關文章之間的得分�,得分越高,說明相關性越大
這里我們定義一個搜索模塊類�����,名為 SearchEngine����,類中有一個核心函數(shù) search 用于查詢搜索
def search(self, query):
BM25_scores = {}
# 對用戶輸入分詞
# 并將其變成 {word: frequency, ...} 的形式
query = jieba.lcut_for_search(query)
word2freq = self.format(query)
# 遍歷每個詞
# 計算每個詞與相關文章之間的得分(計算公式參考 BM25 算法)
for word in word2freq:
data = self.iindex.get(word)
if not data:
continue
BM25_score = 0
qf = word2freq[word]
df = data['df']
ds = data['ds']
W = math.log((self.N - df + 0.5) / (df + 0.5))
for doc in ds:
doc_id = doc['id']
tf = doc['tf']
dl = doc['dl']
K = self.k1 * (1 - self.b + self.b * (dl / self.AVGDL))
R = (tf * (self.k1 + 1) / (tf + K)) * (qf * (self.k2 + 1) / (qf + self.k2))
BM25_score = W * R
BM25_scores[doc_id] = BM25_scores[doc_id] + BM25_score if doc_id in BM25_scores else BM25_score
# 對所有得分按從大到小的順序排列����,返回結(jié)果
BM25_scores = sorted(BM25_scores.items(), key = lambda item: item[1])
BM25_scores.reverse()
return BM25_scores
到此這篇關于Python實戰(zhàn)之手寫一個搜索引擎的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Python寫搜索引擎內(nèi)容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家����!
您可能感興趣的文章:- Mysql實現(xiàn)簡易版搜索引擎的示例代碼
- MySQL全文索引實現(xiàn)簡單版搜索引擎實例代碼
- 詳細介紹基于MySQL的搜索引擎MySQL-Fullltext
- scrapy+flask+html打造搜索引擎的示例代碼
- python基于搜索引擎實現(xiàn)文章查重功能
- Python大批量搜索引擎圖像爬蟲工具詳解
- 360搜索引擎自動收錄php改寫方案
- php記錄搜索引擎爬行記錄的實現(xiàn)代碼
- Python無損音樂搜索引擎實現(xiàn)代碼
- 基于 Mysql 實現(xiàn)一個簡易版搜索引擎