本文主要介紹了OpenCV 圖像對比度,具有一定的參考價值�����,感興趣的可以了解一下
實現(xiàn)原理
圖像對比度指的是一幅圖像中明暗區(qū)域最亮的白和最暗的黑之間不同亮度層級的測量���,即指一幅圖像灰度反差的大小��。差異范圍越大代表對比越大���,差異范圍越小代表對比越小。設置一個基準值thresh����,當percent大于0時,需要令圖像中的顏色對比更強烈�����,即數(shù)值距離thresh越遠�����,則變化越大���;當percent等于1時���,對比強到極致���,只有255和0的區(qū)分;當percent等于0時���,不變;當percent小于0時��,對比下降��,即令遠離thresh的數(shù)值更近些��;當percent等于-1時�,沒有對比了,全是thresh值���。
對比度調(diào)整算法的實現(xiàn)流程如下:
1.設置調(diào)整參數(shù)percent���,取值為-100到100,類似PS中設置��,歸一化后為-1到1。
2.針對圖像所有像素點單個處理�����。當percent大于等于0時���,對比增強�����,調(diào)整后的RGB三通道數(shù)值為:
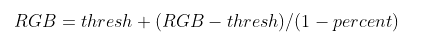
3.若percent小于0時���,對比降低,此時調(diào)整后的圖像RGB三通道值為:
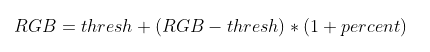
4.若percent等于1時�,大于thresh則等于255,小于則等于0����。
至此,圖像實現(xiàn)了明度的調(diào)整���,算法邏輯參考xingyanxiao���。C++實現(xiàn)代碼如下�����。
功能函數(shù)代碼
// 對比度
cv::Mat Contrast(cv::Mat src, int percent)
{
float alpha = percent / 100.f;
alpha = max(-1.f, min(1.f, alpha));
cv::Mat temp = src.clone();
int row = src.rows;
int col = src.cols;
int thresh = 127;
for (int i = 0; i row; ++i)
{
uchar *t = temp.ptruchar>(i);
uchar *s = src.ptruchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j col; ++j)
{
uchar b = s[3 * j];
uchar g = s[3 * j + 1];
uchar r = s[3 * j + 2];
int newb, newg, newr;
if (alpha == 1)
{
t[3 * j + 2] = r > thresh ? 255 : 0;
t[3 * j + 1] = g > thresh ? 255 : 0;
t[3 * j] = b > thresh ? 255 : 0;
continue;
}
else if (alpha >= 0)
{
newr = static_castint>(thresh + (r - thresh) / (1 - alpha));
newg = static_castint>(thresh + (g - thresh) / (1 - alpha));
newb = static_castint>(thresh + (b - thresh) / (1 - alpha));
}
else {
newr = static_castint>(thresh + (r - thresh) * (1 + alpha));
newg = static_castint>(thresh + (g - thresh) * (1 + alpha));
newb = static_castint>(thresh + (b - thresh) * (1 + alpha));
}
newr = max(0, min(255, newr));
newg = max(0, min(255, newg));
newb = max(0, min(255, newb));
t[3 * j + 2] = static_castuchar>(newr);
t[3 * j + 1] = static_castuchar>(newg);
t[3 * j] = static_castuchar>(newb);
}
}
return temp;
}
C++測試代碼
#include opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
cv::Mat Contrast(cv::Mat src, int percent);
int main()
{
cv::Mat src = imread("5.jpg");
cv::Mat result = Contrast(src, 50.f);
imshow("original", src);
imshow("result", result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
// 對比度
cv::Mat Contrast(cv::Mat src, int percent)
{
float alpha = percent / 100.f;
alpha = max(-1.f, min(1.f, alpha));
cv::Mat temp = src.clone();
int row = src.rows;
int col = src.cols;
int thresh = 127;
for (int i = 0; i row; ++i)
{
uchar *t = temp.ptruchar>(i);
uchar *s = src.ptruchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j col; ++j)
{
uchar b = s[3 * j];
uchar g = s[3 * j + 1];
uchar r = s[3 * j + 2];
int newb, newg, newr;
if (alpha == 1)
{
t[3 * j + 2] = r > thresh ? 255 : 0;
t[3 * j + 1] = g > thresh ? 255 : 0;
t[3 * j] = b > thresh ? 255 : 0;
continue;
}
else if (alpha >= 0)
{
newr = static_castint>(thresh + (r - thresh) / (1 - alpha));
newg = static_castint>(thresh + (g - thresh) / (1 - alpha));
newb = static_castint>(thresh + (b - thresh) / (1 - alpha));
}
else {
newr = static_castint>(thresh + (r - thresh) * (1 + alpha));
newg = static_castint>(thresh + (g - thresh) * (1 + alpha));
newb = static_castint>(thresh + (b - thresh) * (1 + alpha));
}
newr = max(0, min(255, newr));
newg = max(0, min(255, newg));
newb = max(0, min(255, newb));
t[3 * j + 2] = static_castuchar>(newr);
t[3 * j + 1] = static_castuchar>(newg);
t[3 * j] = static_castuchar>(newb);
}
}
return temp;
}
測試效果

圖1 原圖

圖2 參數(shù)為50的效果圖

圖3 參數(shù)為-50的效果圖
通過調(diào)整percent可以實現(xiàn)圖像對比度的調(diào)整���。
到此這篇關(guān)于OpenCV 圖像對比度的實踐的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)OpenCV 圖像對比度內(nèi)容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家!
您可能感興趣的文章:- opencv調(diào)整圖像亮度對比度的示例代碼